Urinary tract infection: recognize and treat it
Better understand the low urinary tract infection (cystitis)
Frequently desire to pee, burn in urination ... One in two women will suffer from at least one episode of symptomatic urinary tract infection during her life.As banal as they are benign, you will have "quickly done" to sweep a "good old" cystitis with antibiotics.But a urinary trainee infection can spread by ascending route to the kidneys.And there it is another pair of sleeves.Explanations.
Definition: What is a urinary tract infection?
Urinary infection is defined by the presence of an infectious agent in the urine associated with certain characteristic symptoms: frequent and urgent need to urinate, burns during urination, difficulty emptying your bladder ... "The diagnosis of'Urinary tract infection is made up when an ECBU examination reveals the presence of germs in the urine ", according to Doctor Schérifa Salifou Laurain, general practitioner.
Indeed, in healthy individuals, the urine present in the bladder is sterile and does not contain microorganisms.In addition, the duct that conveys urine from the bladder to the outside of the body (called urethra) can contain bacteria but these are in too small to cause an infection.However, it may happen that an infectious agent affects the lower end of the urinary tract (the external urethral meatus located at the end of the penis in men and at the vulva in women).It is then the triggering of an infection which will extend by ascending route by going up towards the lower then upper urinary tract.
Depending on the location of the infection, we speak:
The treatment of a urinary tract infection depends on the causal infectious agent and its location.
More frequent urinary tract infections (IU) in women
Urinary infections (IU) are the most common bacterial infections in women: 50% of women will suffer from at least one symptomatic episode during their life (source 1).A third of women who have had a first episode of IU will suffer from recurrent urinary tract infections.Urinary infections occur in 20% of cases in humans (source 1).
Urinary infections at any age
Women between 20 and 50 years old is more at risk of developing urinary tract infections.In humans, it is the opposite: urinary tract infections increase from 50 years, due to a high proportion of prostatitis.In children, urinary tract infections are rarer, a secondary urine malformation often exists.
Complications related to urinary tract infections
"Today, we no longer distinguish urinary tract infections depending on whether they are low or high but rather depending on whether they are simple or at risk of complications", according to Doctor Schérifa Salifou Laurain, general practitioner.Urinary infections present a risk:
There are certain risk factors predisposing to these complications such as: diabetes, immunosuppression, pregnancy, history of pyelite / calculation / anomaly of the excretory tracks, a remaining or transient probe in place, a recent urological intervention, an infectionUrine acquired in the hospital, male sex, advanced age, recent antibiotic treatment, recurrent infections (≥4 episodes/year) ....
À lire aussiWhat are the different forms of urinary tract infections?
The type of urinary tract infection depends on its location:
Lower urinary tract infections (IUB)
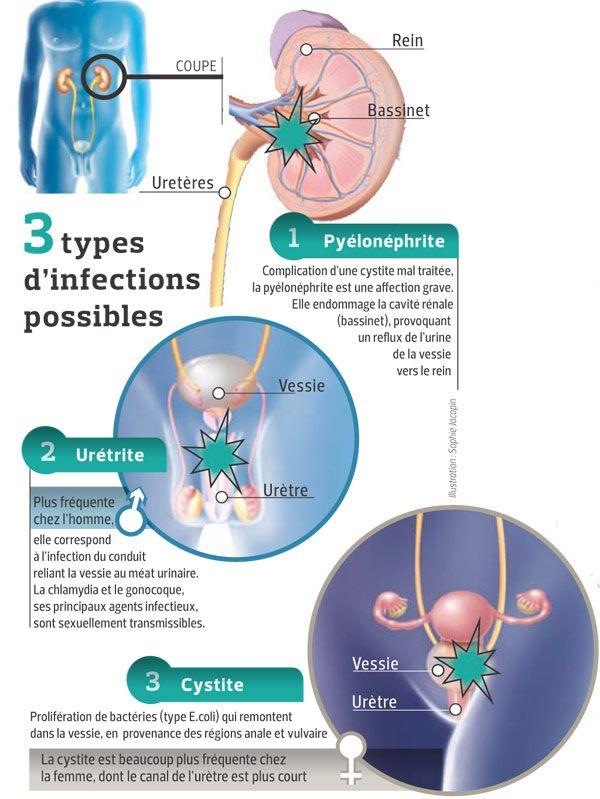
They are located in the low urinary tract.
High urinary tract infections (IUH)
They are located in high urinary tract.
À lire aussiHow is a urinary tract infection trigger?
Low urinary tracts, an infectious entrance door
Urinary tract infection is linked to the intrusion of microorganisms (most often bacteria) by the lower end of the urinary tract: the external urethral meatus, which is found in men at the end of the penis and inwomen in the vulva.
The infection then develops upwards through the urethra to the bladder, and sometimes to the kidneys.However, there is a second possible gateway: blood circulation, generally up to the kidneys.
Dr Itzel Ocampo, Medical Director for https://t.co/hk3fbhimqc Talks about How to Holden Balanced Diet During Quer… https://t.co/q4bshpkqim
— 21Milliondoc 📲👨⚕️👩⚕️🆓 Sat Apr 18 05:13:26 +0000 2020
Contamination by the infectious agent can be done during a sexual intercourse or even in the event of maceration, lack or on the contrary of excess of intimate hygiene (the lack of hygiene promotes the presence of intestinal bacteria at the level ofUrinary tract. Excess hygiene attacks the genital flora and promotes the proliferation of fungi or mycoses), complications of recent urological medical gestures ...
À lire aussiA bacterial origin, most often
Urinary infections (IU) are almost always of bacterial origin, although viruses, fungi and parasites can also infect the urinary tract.More than 85 % of IUs are caused by bacteria from the intestine or vagina (source 2).
Escherichia coli is the bacterial agent most frequently causing an IU. Other bacteria contracted during sexual intercourse is also involved: chlamydia, gonococcus, mycoplasm ... Finally, the bacillus of koch (tuberculosis) can also give rise toa urinary tract infection.
What are the risk factors for urinary tract infection?
What are the symptoms of a urinary tract infection?
Urinary infections sometimes appear without symptoms.However, most of the time, they manifest themselves in different signs depending on the location of the infection.
Symptoms of low urinary tract infection (cystitis, uretritis, prostatitis ...)
The usual symptoms are:
The patient generally does not have a fever if it is a simple cystitis.On the other hand, a patient with prostatitis may have fever, pressure in the rectum or blood in the sperm (in humans).In addition in the case of urethritis, urethral flow and leukorrhea (or white losses) can be observed.These last two affections are also sometimes at the origin of sexual disorders (pain during sexual intercourse or during ejaculation (in humans), erection disorder ...).
Symptoms of high urinary tract infection (pyelonephritis, pyelite)
In case of renal infection symptoms (or pyelonephritis), it is recommended to consult a doctor quickly:
Symptoms of urinary tract infection in children
The child sometimes presents atypical symptoms of urinary tract infection: a fever associated or not with stomach aches, night incontinence (or enuresis) ... In young children and infants, urinary tract infection can be detected bycrying during urination, fever, irritability ...
À lire aussiSymptoms of urinary tract infection in the elderly
The elderly can feel atypical symptoms: fever, urinary incontinence, digestive disorders, loss of appetite ...
How can we prevent urinary tract infection?
In order to prevent the occurrence of a urinary tract infection, it is necessary to:
The effectiveness of cranberry juice, often recommended for the prevention of urinary tract infections, would not be scientifically validated, according to the latest studies.Liters of juice would be necessary to hope to obtain any protective effect.In women with chronic urinary tract infections, cranberry could however be of interest, if the active ingredient is sufficiently dosed.
On video: How to avoid repeated urinary tract infections?
How is the diagnosis of urinary tract infection?
To establish the diagnosis of urinary tract infection, the doctor can perform a first test thanks to a urinary strip.The examination is supplemented by a cytobacteriological examination of the urine (ECBU) which makes it possible:
À lire aussiIf a bacteria is identified at the end of the ECBU, a study of its sensitivity to different antibiotics (antibiogram) is carried out.She guides your doctor in her prescription of antibiotics.
High or low IU: What treatments?
The treatment of urinary tract infections is based on the use of antibiotics for a variable period depending on the type of infection.
Simple Low Urinary Infections Treatments (IUBS)
IUBS as cystitis or urettite are treated by oral antibiotic therapy:
As a first intention:
In second intention: Quinolones for 3 days (Norfloxacin 2x400 mg/d).
In the event of a relapse, it is necessary to establish a longer treatment (7 days), suitable for the antibiogram, and possibly seek an anatomical cause.In case of reinfection, you have to look for an exogenous cause (like too frequent sex, the use of spermicidal cream for example).
Une prophylaxie antibiotique est parfois proposée aux récidives fréquentes (>4 épisodes/an) et invalidantes, ce en raison du risque de sélection de germes résistants et des éventuels effets secondaires.
À lire aussiComplicated bass urinary tract treatments (IUBC)
In the event of IUBC, a urine culture must be carried out in order to adapt the tailor -made treatment.The doctor prescribe without waiting for the results of the cultivation of nitrofurantoine (3x100 mg/d for 5-7 days) or quinolones (such as norfloxacin 2x400 mg/d for 7 days).Treatment is reassessed after receiving culture and antibiogram.
Simple Urine Infections Treatments (IUHS)
In the event of simple acute pyelonephritis, treatment can be conducted by outpatient, hospitalization remains necessary in the event of signs of generalized infection (SEPSIS) or incapacity to take oral treatment.
Antibiotic treatment should be started immediately and will be changed if necessary as a function of the antibiogram results.The doctor may prescribe the choice:
Telephone control or the office with the patient at 48-72 hours after the start of treatment is always necessary.A culture is not carried out after the end of treatment if the symptoms have disappeared.
Complicated high urinary tract treatments (IUHC)
In case of IUHC, a urine culture is carried out.The first -line treatment remains ciprofloxacin (2x500 mg/d), which must be reassessed after receiving the results of the culture and the antibiogram.Hospitalization may be necessary in the event of acute symptoms.
What complementary approaches in the event of urinary tract infection?
Phytotherapy, aromatherapy and homeopathy, can be useful during a urinary tract infection.
In phytotherapy
In infusion: Put 3 teaspoons of business in 1 liter of boiling water.Boil for 5 minutes.Leave to infuse another 5 minutes.Filter.Drink 3 cups a day for 1 week.
After numerous controversies on the effectiveness of cranberry in the prevention and treatment of urinary tract infections, it is admitted that it can be useful in prevention of recurrences in women suffering from at least four annual infections, provided thatIt is sufficiently dosed (its active compound must be present up to 36 mg).
In aromatherapy
- Apply 2 drops of sandalwood essential oil on the lower abdomen.3 to 5 times a day for 5 days;- Pour 1 drop of savory essential oil into a teaspoon of olive oil.Let melt in the mouth.4 times a day for 5 days. Extract from my secrets as a pharmacist, Danièle Festy, ed.Leduc.s.
In homeopathy
- During irritation, burn by urinating: 2 cantharis granules 5 hp, 3 times a day;- During chronic urinary tract infections: 2 colibacillinum 4 hp granules, 3 times a day or 2 granules of anticolibacillary serum 5, 3 times a day.
Interview with Doctor Schérifa Salifou Laurain, general practitioner.
Source 1: "Urinary infections", A. François and Al., Geneva University Hospitals.
Source 2: "Presentation of urinary tract infections (IVU)", Talha H. Imam, MD, University of Riverside School of Medicine, February 2020.
A lire aussi